In this article we will
talk about three asteroids. Two of these objects recently flew past Earth,
while a third asteroid is on the way and will arrive on February 15, 2013.
Astronomers periodically find new asteroids, and there are tables which
list all significant upcoming asteroid flybys. In the past, these tables
used Astronomical Units AU as the measurement reference for asteroid flyby
distance. One AU is the distance of the Earth to the Sun, or about 93
million miles. Now these same tables list far closer objects with most
objects using the average distance of the Earth to the Moon (238,857 miles).
This is officially known as the Lunar Distance, LD. You will see this
term in this article. Technology has made it possible to detect more smaller
asteroids than ever before.
On December 12, 2012 a large, potentially hazardous asteroid flew through
Earth's orbital path, 4179 Toutatis.
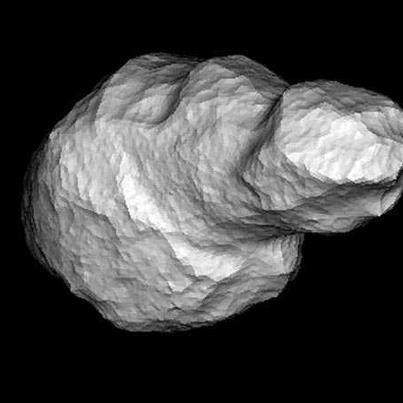
Asteroid Toutatis
This massive object measured 8,858 ft. across and missed the Earth by
18 LD which equates to 4.3 million miles. Despite the large distance
from Earth and being less than two miles across, Toutatis was visible
with a small telescope.
On December 11, 2012 a lesser known asteroid passed by Earth known as
2012 XE54. It measured 32 meters (104 ft.) long using radar imaging (radar
images below.) It passed just .6 LD. Multiplying LD x .6 shows that
asteroid 2012 XE54 passed by Earth just 143,314 miles away. While this
object may seem far away, consider that this asteroid is traveling through
space at 13km/sec carrying the equivalent energy of a 1 megaton blast.

Asteroid 2012 XE54 which missed Earth on December 11, 2012
Yet another asteroid named 2012 DA14 will pass near Earth on
February 15, 2013:

Getty Images - Asteroid 2012 DA14 coming February 2013
2012 DA14 will pass by Earth much closer than the previous smaller asteroid.
2012 DA14 will pass just .09 x LD, which equates to 21,497 miles away.
When it flies past Earth it will be under the influence of the Earth's
gravitational field. Most experts do not believe 2012 DA14 will hit Earth.
2012 DA14 Specs:
* Mass: 130,000 tons (a bit heavier than a grand piano)
* Speed: 10.6 miles/second
* Size: 57 meters (187 ft.)
* Energy: 2.7 megatons
Asteroid velocity and energy will increase proportionately upon entering
the influence of Earth's gravitational field.
Telephone and television satellites are parked in geostationary orbits
in the Clarke Belt at 22,500 miles with less than two degree spacing.
The belt is named after Arthur C. Clarke. He came up with the idea of
parking satellites at that distance from Earth while establishing the
correct velocity. This invisible sweet spot around Earth is called a geostationary
orbit, and allows satellites to operate there almost indefinitely, requiring
very little energy to keep it from drifting.
2012 DA14 will pass THROUGH our communication satellite belt twice:
First time - On its way toward Earth
Second time - back through the belt again on its way out.
Angle at which the object 2012 DA14 enters and leaves the Clarke Belt
will determine the likelihood of taking out one or more satellites. Both
events will happen quickly due to the velocity of the asteroid at 10.6
miles/second - 38,160 miles/hour before acceleration by Earth's gravity.
This is about 2.6 times faster than the space station.
QUICK GUIDE TO SATELLITES AND HOW THEY WORK
Geostationary satellites can only remain in orbit by sustaining the correct
velocity. The first step to reaching the correct velocity is either from
a launch from the orbiting shuttle's payload bay or by a rocket
launch. For box-shaped satellites with extendable solar panel wings such
as those used by Dish Network, a large flywheel is spun up by a motor
just before the satellite is ejected either from the payload bay or from
a rocket.
For cylindrical satellites, the entire satellite is spun up like a top
to about 50 RPM. The entire outer shell of the satellite telescopes outward
in several sections, extending the length from about 9 ft. to more than
27 ft. Each telescoping section is covered in solar cells. A precision,
long life motor mounted on top of the satellite has a dish antenna mounted
on the motor's shaft. This motor counter-rotates in the opposite direction
at 50 RPM to keep the antenna motionless and pointed toward Earth.
For both satellite types, after reaching low Earth orbit a rocket motor
(known as an apogee kick motor) on the satellite burns for a precise amount
of time to move it into it's exact orbital slot and make the orbit circular.
Small gas thrusters and/or flywheel braking are periodically used to precision
adjust for drift. Satellite velocity must perfectly match the velocity
of the Earth' surface to keep it stationary in space. This allows fixed
satellite dishes everywhere on Earth to work year after year.
Satellites use the same principal as a toy gyro to stay properly oriented.
Flywheels on magnetic bearings remain spinning in the friction free vacuum
environment for the life of the satellite. The slightest tap or brush
with an asteroid can cause a satellite to tumble out of control, much
like when you touch a spinning toy top. This can force the satellite's
antenna to randomly point to anywhere in deep space. When this happens,
both control signals and communications signals will be lost.
How carefully are satellites aimed at Earth? Each satellite's antenna
is designed to provide coverage to a specific area. Usually satellites
are aimed at the Nebraska-Kansas area for television and communications
coverage over the lower 48 states. Now imagine aiming an antenna on a
satellite from an Earth control station at one of these states from 22,500
miles away.
Asteroid debris reaching the space station could be disastrous. Fortunately,
the space station flies in a low Earth orbit approximately 200 miles up.
It is unknown what other rocks 2012 DA14 may have traveling along with
it towards Earth. A tiny pebble smaller than a No. 2 pencil eraser can
destroy any satellite if it has sufficient velocity.
WHAT ARE THE IMPLICATIONS OF AN ASTEROID IMPACT WITH EARTH?
All three of these asteroids are registered as "Potentially Hazardous
Asteroids" (PHA.) Fortunately Toutatis is the biggest one of these three
asteroids which can wipe out life on Earth, and it remains far away. Asteroids
earn PHA classification by a combination of Earth-crossing orbit, a certain
size and velocity. All these characteristics combine together can enable
a PHA to destroy a continent or even the entire Earth. Fortunately, 2012
DA14 and 2012 XE54 are not large enough to cause global or continental
damage.
For larger asteroids, water impact simulations show an ocean impact will
cause massive tsunamis towering a mile high or even more. Some computer
models have shown that two massive tsunamis can be generated upon impact
with an ocean and travel outward in opposite directions. These giant waves,
which have never been seen in the history of the world can circle the
globe. Eventually they will collide with each other on the opposite side
of the Earth. There they will reverse direction and returning back to
the asteroid point of impact and collide again. It is hard to comprehend
short term and long term effects this would have on most of the world's
major cities which are located on coastal areas.
A ground impact will be far worse. Scientists have modeled a ground-impacting
asteroid. This type of impact will have far more devastating effects on
life. Millions of tons of dirt and dust will be blasted into the upper
atmosphere. There it will continue to circle the Earth for months, blocking
out most of the Sun's light for up to one year. Trees and crops will die
after three days if there is insufficient sunlight for photosynthesis.
Cities can be rebuilt and people relocated after a asteroid-created super-tsunami.
But losing all of Earth's trees and crops from a strike on land will wipe
out both land and ocean ecosystems, destroying all life around the globe.
Even oceans can die from a large asteroid impact on land. Plankton is
at the base of the ocean food chain and it too, must have sunlight.
In either case, there is the serious issue of shifting the axis of Earth's
rotation and altering the wobble. These are entire subjects in themselves
and are outside the scope of this article.
Anyone who survives the effects of a large mile wide (or larger) asteroid
strike will soon turn feral. A domestic house will turn feral when kept
outside for just two weeks. People will resort to robbery, killing and
cannibalism in a very short time after all the food is gone. When a plane
crashed high in the Andes mountains many years ago, it was cannibalism
of those who died which kept remaining passengers alive through the winter.
Even though these people knew that eventually they would be rescued when
spring came, the pain of starvation and accompanying symptoms was too
much for anyone to endure. Now imagine the survival mentality an asteroid
strike will create in everyone - seeing civilization as we know it wiped
out, no food, electricity, running water, medicine, doctors, hospitals,
etc... ever again. Even a simple injury could become infected and life
threatening.
When trees and plants have died they cannot be replaced. Even if there
were trillions of seeds or seedlings ready to re-plant the Earth, there
would not be enough sunlight or oxygen to germinate the new plants and
these would also die. Atmospheric CO2 levels for those that survive will
rapidly rise without trees to recycle CO2 into oxygen around the world
every day. Forget about global warming - all life on Earth will suffocate
without oxygen-recycling by trees and plants.
That big seed vault in Norway? It is completely useless without sunlight.
It cannot hold enough seeds to repopulate all the trees needed to make
Earth livable again. There is also the matter of bees. Without bees to
do the pollination of plants and crops, plants cannot produce fruit or
vegetables. Did they store billions of bees in the Norway vault? Probably
not. It would seem that the Norway vault is just a mental exercise to
feel good for some. When things become so bad that the vault must be opened
and seeds used - where will the bees come from for plants to grow?
It would take hundreds of years for the world to have trees and bees once
again, long after the atmosphere cleared and our Sun shines again. People
would have to re-plant all the trees on the planet, starting with seeds.
Then use those seeds to make seedlings, etc... But no one would be around
to do it because of the lack of oxygen and food, and destruction of civilized
life as we know it. Our entire comfortable, civilized world is hanging
by a very delicate thread. When technology is broken it may be impossible
to repair. Within a few years words like Facebook, internet, emails and
texting will vanish from everyone's vocabulary. Survival will be a 24/7
issue for as long as it can go on.
Wasn't all that uplifting? Gives you a new appreciation for the modern
life we have today. Hopefully 2012 DA14 will pass by and nothing serious
will happen to dozens of complex, hard-to-replace, expensive communication
satellites which have become the backbone of our civilization.
What happens if a larger asteroid than 2012 DA14 becomes a serious threat
to life on Earth and we cannot stop it? Is there an alien race out there
that will prevent a collision? Perhaps someone will alter the trajectory
of 2012 DA14 and it won't even pass through the Clarke Belt. If they did,
it would provide undeniable proof someone is out there looking out for
us. Or maybe some mouthpiece will blame the trajectory change on swamp
gas...
|
![]()